Key features
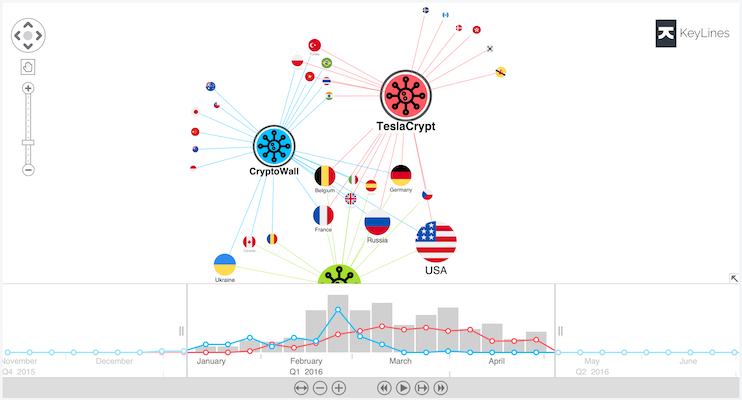
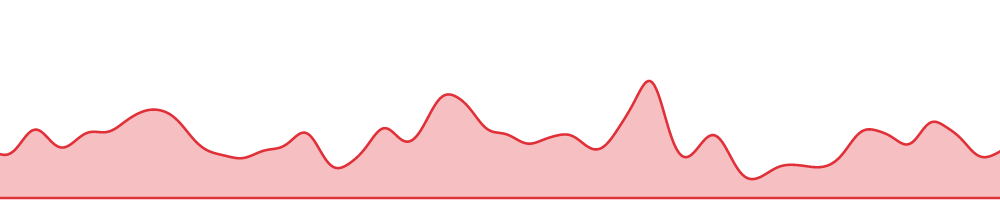
There are two ways that you can display data in the time bar:
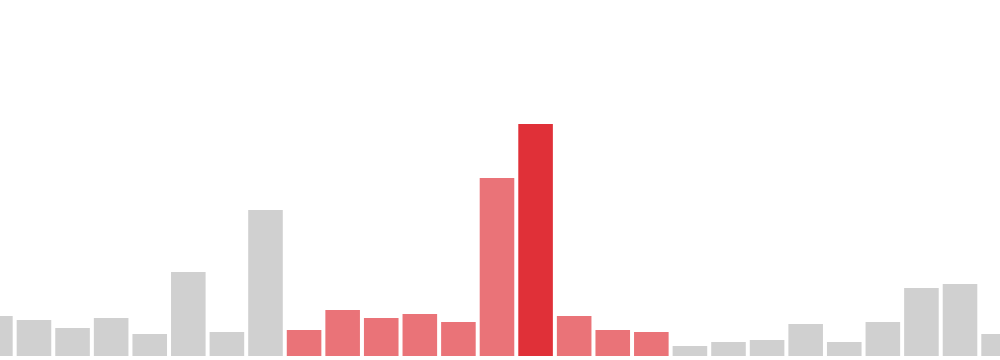
Histogram
Each bar represents a period in time and is a cumulative count of all items within the range. Selection lines do the same, but on a different (usually sub)set of data.
Histogram bars can also display groups of data within them as a set of stacked bars.